Study of natural background radiation in Reiche Zeche and Alte Elisabeth shafts (Freiberg, Germany)
The Reiche Zeche mine is a historical ore mine and is one with six underground locations which participate in the BSUIN project. Underground Laboratory is located in the eastern part of the Erzgebirge Mountains within the Innerer Freiberger Gneis (Freiberg, Saxony, Germany). This mine is Research and Teaching Mine of Technical University Bergakademie Freiberg (TUBAF). In the mine are two shafts Reiche Zeche and Alte Elisabeth. In-situ measurements of natural background radiation (NBR) in Reiche Zeche (1st level at a depth of 150 m) and Alte Elisabeth shafts were performed in December 2018 and March 2018, respectively, by a group from the University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland. From the same localizations samples of water and rock were collected for laboratory analysis of uranium and radium concentrations.
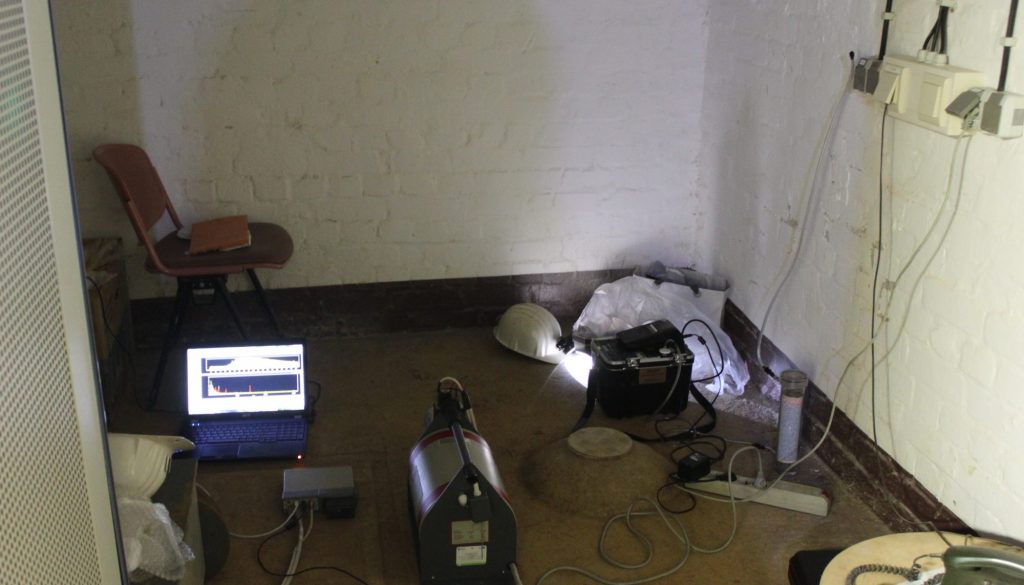
At the Reiche Zeche mine (two localization: Reiche Zeche-server room and Alte Elisabeth-rock cavern) the following measurements were performed: in-situ gamma ray spectrometry based on high-purity germanium detector (HPGe Fig. 1) and radon concentration in air by use of RAD7 (Durridge) detector (Fig. 2).


Figure 1. In-situ HPGe measurements in two studied localization: rock cavern near Alte Elisabeth shaft (left) and in the server room near Reiche Zeche shaft (right).

Figure 2. Rad7 radon detector during measurements in Alte Elisabeth shaft.
The measurements of rock samples were carried out also by using gamma spectrometry technique (HPGe detector) in the Low-activity Laboratory of Nuclear Physics and Its Applications Department of Institute of Physics in the University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland. Rock samples were crushed and prepared for laboratory gamma spectrometry measurement in Marinelli baker; prepared for uranium content analysis and activated in 252Cf neutron source for 1 month. Comparison of gamma energy spectra which underwent detailed analysis is presented in Fig. 3 and detailed characteristics of in-situ registered spectra is presented in Fig. 4.
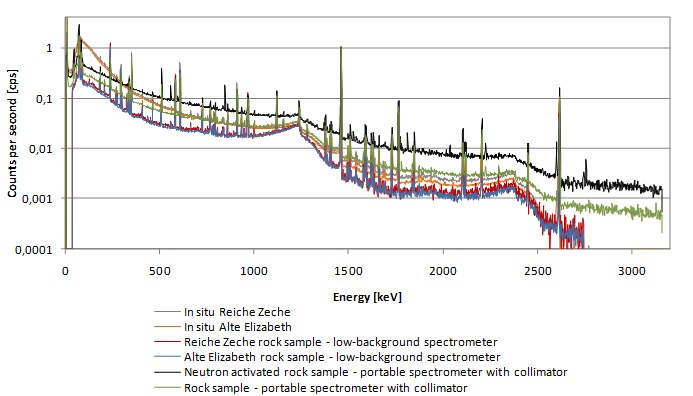
Figure 3. Comparison of registered gamma-ray spectra which underwent detailed characteristics.
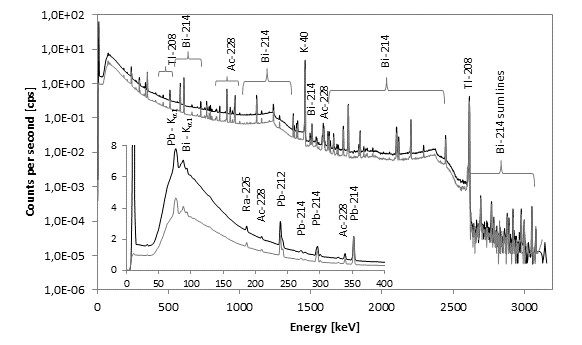
Figure 4. Qualitative analysis of in-situ registered spectra in Reiche Zeche (gray line) and Alte Elisabeth (black line) locations.
Radon in-air concentration in the server room has been monitored in two measurement cycles: 24 measurements 1h-long each. Detector was placed in the right and left corner of this room. Right side measurements were started at 11 a.m., whereas left side measurements at 12 a.m. Variation of radon concentration over 24 h is presented in Fig. 5, with the global mean value of 869 ± 24 Bq/m3 and median of 833 Bq/m3. The differences between two studied locations is probably due to the ventilation duct.
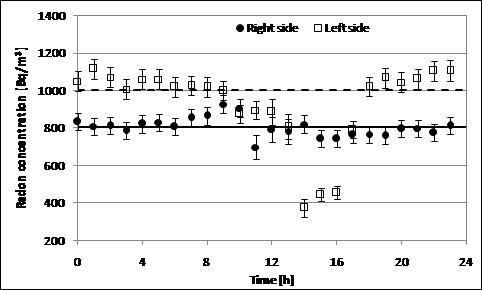
Figure 5. Radon concentration monitoring in server room near Reiche Zeche shaft in December 2018.
The water samples from Reiche Zeche and Alte Elisabeth shafts were analyzed for uranium and radium concentration. The measurements of radium (226,228Ra) activity concentrations were performed with the use of the 1414 WinSpectral α/b liquid scintillation counter from Wallac (Fig. 6 left). The activity concentration of radium isotopes were below minimum detectable activity (MDA is equal to 0.01 Bq/l and 0.03 Bq/l for 226Ra and 228Ra, respectively, for 3600 s counting time and 2 l of water initial sample volume). The measurements of uranium isotopes (234,238U) were performed with the use of α – spectrometer 7401VR from Canberra – Packard equipped with the Passivated Implanted Planar Silicon detector with a surface area of 300 mm2 (Fig. 6 right). Water samples were measured over a period of 2-3 days. The chemical recoveries were equal to 76% and 60% for Reiche Zeche and Alte Elisabeth water samples respectively. Minimum Detectable Activity (MDA) is equal to 0.5 mBq/l for both 234,238U isotopes and 0.5 l initial sample volume.


Figure 6. Measurement devices: 1414 WinSpectral α/b liquid scintillation counter from Wallac (left) and α-spectrometer 7401VR from Canberra – Packard (right).
Data with calculated concentration uranium radium and potassium in water and rock samples was presented in Table 1.
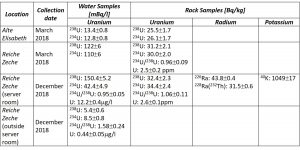
Table 1. Uranium, radium and potassium concentration in water and rock samples collected in Reiche Zeche and Alte Elisabeth shafts.




